Comparison of the advantages of NB-IoT and LoRa in the Internet of Things
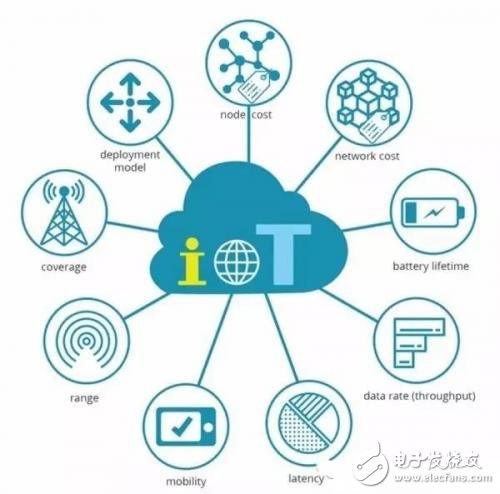
IoT applications need to consider many factors, such as node cost, network cost, battery life, data transfer rate (throughput rate), latency, mobility, network coverage, and deployment type. It can be said that no technology can meet all the needs of IoT. The NB-IoT and LoRa technologies have different technical and commercial features, so there will be differences in application scenarios. Here, the differences between the two will be explained, and the applicable application scenarios will be described.
What are the advantages of NB-IoT?
As a technology applied in low-rate services, the advantages of NB-IoT are not difficult to imagine:
• Strong links: In the case of the same base station, NB-IoT can provide 50-100 times more access than existing wireless technologies. One sector can support 100,000 connections, supporting low latency sensitivity, ultra-low device cost, low device power consumption, and optimized network architecture. For example, due to bandwidth limitation, operators only open 8-16 access ports for each router in the home, while a family often has multiple mobile phones, laptops, and tablets. In the future, it is necessary to realize the whole house intelligence. The need for networking across hundreds of sensing devices has become a daunting challenge. And NB-IoT is enough to easily meet the needs of a large number of devices in the future smart home networking.
• High coverage: NB-IoT has strong indoor coverage and 20dB gain over LTE, which is equivalent to an increase of 100 times coverage. Not only can it meet the wide coverage needs of rural areas, but also for applications such as factory areas, underground garages, and manhole covers that require deep coverage. Take the manhole cover monitoring as an example. In the past, the GPRS method required an antenna to be extended, and the vehicle was extremely vulnerable to damage. The NB-IoT can solve this problem as long as it is properly deployed.
• Low power consumption: Low power consumption is an important indicator for IoT applications, especially for equipment and occasions where batteries cannot be replaced frequently, such as various types of sensing monitoring equipment placed in remote areas of the high mountains and wilderness. When a smartphone is charged every day, battery life for several years is the most essential requirement. NB-IoT focuses on small data volume and small rate applications, so the power consumption of NB-IoT devices can be very small, and the battery life can be greatly improved from the past few months to several years.
• Low cost: Compared to LoRa, NB-IoT does not need to be rebuilt, and both RF and antenna are basically multiplexed. Taking China Mobile as an example, there is a relatively wide frequency band in 900MHZ. Only a part of the 2G frequency band needs to be cleared, and the simultaneous deployment of LTE and NB-IoT can be directly performed. Low speed, low power consumption and low bandwidth also bring low cost advantages to NB-IoT chips and modules. The module is expected to cost no more than $5.
Guangzhou Yunge Tianhong Electronic Technology Co., Ltd , https://www.e-cigarettesfactory.com