In-depth analysis: LED lighting heat dissipation and adjustable thermal protection technology
Along with the rapid development of the LED lighting market, the LED lighting application related products are becoming lighter and thinner, and the power demand is more powerful. Among them, the heat dissipation performance requirements are increasingly severe. In addition, the failure rate of the LED power module is also improved with the limited heat dissipation performance of the lamp material. Therefore, the thermal protection sensing technology related to the LED lighting control IC has recently become a hot spot for the design and application of various LED lamps.
LED lamp cooling problem
In general, conventional LED lamps use aluminum heat-dissipating materials as the lamp housing. Although they have good heat dissipation effects, they are complicated in processing, high in cost, and heavy in materials. In the principle of heat dissipation of LED lighting fixtures, the heat conduction mechanism of the carrier through the heat conduction inside the material is required.
Among them, the metal heat conduction is mainly because the metal has free electrons and can transfer heat energy quickly; while the plastic has no free electrons, the molecular vibration is difficult, and the heat conduction is mainly the result of the lattice vibration of the material itself, and the phonon is the main thermal energy loader.
In contrast, the plastic lamp housing has other advantages in design, performance and cost, such as light weight (20-40% lighter than aluminum), easy to form, low cost, and the most important feature is that the plastic is not conductive. With good electrical insulation, it is a general trend for non-isolated LED lighting drivers to use plastic housings.
However, the thermal conductivity of plastics is generally poor, and the resin type materials directly affect the thermal conductivity. Generally, the thermal conductivity k of plastics is generally only 0.2 W/(m*K), which is about 1/1000 of that of aluminum. Can not effectively dissipate heat and affect the reliability of LED lamps.
LED lamp reliability
The concept of reliability first began in the Second World War. When Germany developed the V-1 rocket, the failure rate of each component directly affected the performance of the entire system. The concept is the same in the power module of the LED luminaire, wherein the change of the ambient temperature causes the reliability of the LED luminaire to be reduced, and the electrolytic capacitor used in the LED and the driving circuit has the greatest influence on the reliability evaluation.
Figure 1 shows the relationship between Tj temperature and life of high-brightness white LED. It can be seen from the figure that the lower the temperature of Tj, the longer the service life. In addition, the relationship between temperature and service life of electrolytic capacitor device in Figure 2, electrolytic capacitor in power module. The service life is also inversely proportional to the ambient temperature.
The destruction of the electrolytic capacitor may even cause the lamp to be unusable, so if the lamp can effectively adjust the self-temperature with the sensing ambient temperature, the service life of the LED lamp can be prolonged. Therefore, how to adjust the temperature is an important issue in LED lighting applications.
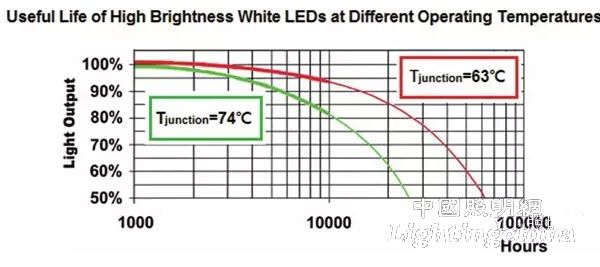
Figure 1 LEDTj temperature and service life relationship diagram
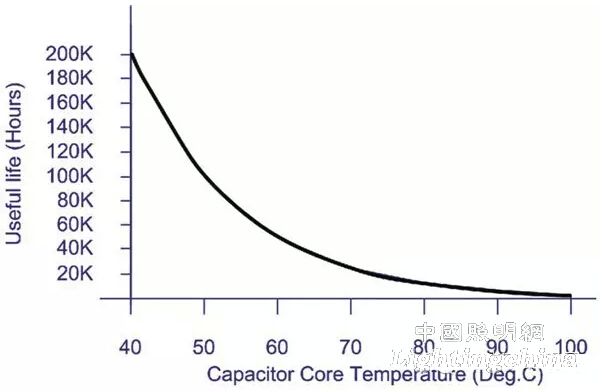
Figure 2 Electrolytic capacitor temperature and service life relationship
Temperature sensing
In practical applications where temperature is sensed, thermistors are the most common and readily available temperature sensors, with the addition of thermistors in LED lamp power modules as an effective and low-cost solution for sensing temperature applications.
The thermistor is made by mixing metal oxides and sintering at a high temperature. The resulting component has the property of changing the resistance value with temperature.
One of the most common types is the negative temperature coefficient thermistor (Negative Tempoefficientthermistor), referred to as NTCThermistor. Its resistance value will decrease as the temperature rises.
Thermistors are used for three major advantages of temperature sensing:
1. It has extremely high sensitivity. If a high-resistance thermistor is used, the sensitivity can be as high as 10kΩ/°C.
2. Its relative high resistance value. Its resistance at 25 ° C can span hundreds to several MΩ selectivity. Its high resistance value reduces the error caused by the impedance of the wire.
3, thermistor provides a variety of component packaging, which is a patch-type minimal shape packaging, and even the size can be reduced to 0201 packaging, as shown in Figure 3. In the circuit design, it can be easily laid out around the components that need to sense the heat source.

Figure 3 Schematic diagram of thermistor package