MCU application in mobile phones and tablets
In current mobile and tablet applications, MCUs are primarily used as coprocessors for functions such as capacitive touch sensing interfaces, touch screen interfaces, camera interfaces, different analog sensor input detection, USB interfaces, and battery charging and monitoring. In addition, all logic and interfaces responsible for interconnecting these functions can be used with ADCs for analog inputs, PWMs for buzzer applications, segment LCDs, character LCDs, graphical LCDs, DACs for volume control. Various usable component modules such as USB interface and capacitive touch screen interface are designed.
This article explores the role of MCUs and Programmable System-on-Chip (PSoC) in mobile and tablet applications, and evaluates system limitations and design challenges for such applications. Programmable devices can reduce overall product cost by reducing BOM cost and design cycle time, and can save project costs by speeding up the development process.
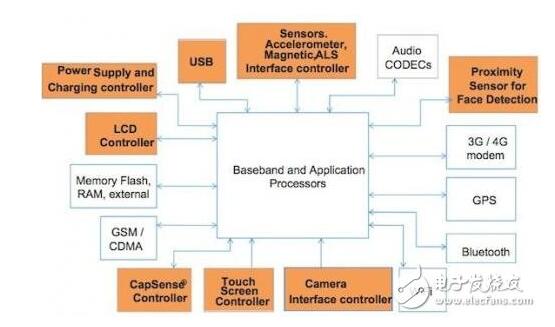
Figure 1 mobile phone design block diagram (Note: the highlighted module is operated by MCU.)
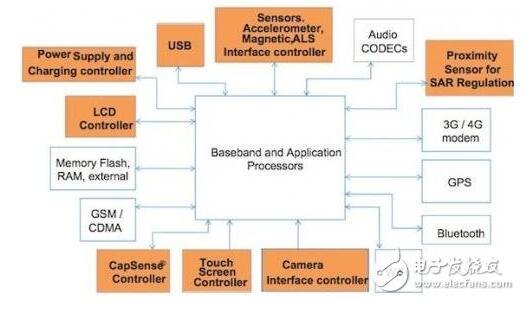
Figure 2 Tablet design block diagram (Note: The highlighted module is operated by MCU.)
Current mobile phones and tablets are designed with 8/16/32-bit MCUs as coprocessors for different functions. For example, an MCU can receive analog input signals from various analog sensors:
Temperature sensors such as thermistors, RTDs and humidity sensors receive analog inputs and provide digital voltages for the MCU.
It is possible to measure 2-axis/3-axis motion and convert it into a 2-axis/3-axis accelerometer for the digital voltage of the MCU.
Ambient Light Sensors (ALS) enable automatic control of the backlight brightness of a wide range of lighting conditions, from dark to direct sunlight.
Magnetic sensor input through external ADC and buffer circuit.
A proximity sensor for face detection and hand motion detection to enable the MCU to turn off the keyboard when the user brings the phone closer to the face. In addition, the MCU can open the keyboard when the user's hand approaches the keyboard. The MCU uses a host interrupt function to activate the wideband and application processor to perform face detection operations. The MCU implements face detection by detecting the proximity of the user's face, ear or head to eliminate false touches of the touch screen. This reduces battery consumption by turning off the touch screen. This feature is implemented using an IR proximity sensor.
Proximity sensing for specific absorption rate (SAR) adjustment in tablet applications. SAR is the rate at which energy is absorbed when the body is exposed to radio frequency (RF) electromagnetic fields. The device needs to dynamically adjust the radio transmission near the human body.
An external buffer drive circuit that drives an LCD or graphic display. LCD or graphic displays with backlights are typically used in low-end mobile applications. In addition, it can control the backlight of the LCD and graphic display.
The MCU uses a touch screen controller to handle touch screen interfaces in high-end mobile applications.
The MCU uses a mechanical keyboard to handle user input in low-end mobile applications.
The MCU monitors the Li-Ion battery voltage and manages battery charging for optimal charge life.
In addition, the MCU can also be used for fault detection and data recovery applications in mobile phones.
The MCU uses HapTIcs (Tactile Feedback Technology) instead of mechanical buttons (which connect users by touch, force, vibration or motion).
The MCU can be connected to broadband and application processors, and can also be connected to other on-board peripherals, such as a camera interface controller connected to the SPI interface via I2C. The MCU connects the broadband and application processors in host (master) and slave modes for data transfer. Broadband and application processors use an on-board USB 2.0/3.0 controller to transfer data externally.
Flat Wire High Current Inductor
Flat Wire High Current Inductor,Small Flat Wire Common Mode Inductors,High Current Flat Wire Inductors,High Power Flat Wire Inductors
Shenzhen Sichuangge Magneto-electric Co. , Ltd , https://www.scginductor.com