The research and development of FPGA engineers - bus research
If there are multiple modules in the design, there are many registers inside each module or the memory blocks need to be configured or provide readout. There are many ways to implement them, mainly as follows:
Implementation 1: The registers can be pulled out at the top of the module to provide a unified module for configuration and readout. This method is simple and simple, but the top-level connection has a large workload, and if the number of configurations is large, the number of registers in the top layer will be larger.
Implementation 2: Connect via the bus and assign an address range to each module. Such extensions such as registers can be extended inside the module without excessive top-level interconnection at the top level. As shown below:
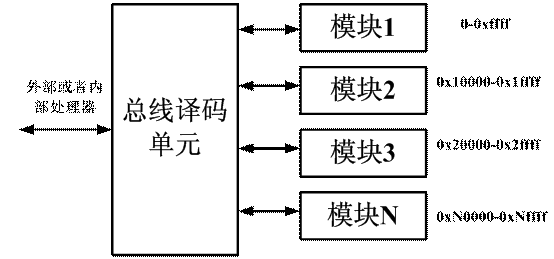
If you choose the bus, then a very simple bus recommendation is used, which is the AVALON-MM bus.
ALTERA proposes two bus types, AVALON-MM.
AVALON-ST. Used to connect memeory and data stream transfers
MM is not what you want, its English is memory map. Implementing memory mapping is the main purpose. The main signals are shown in the following table:
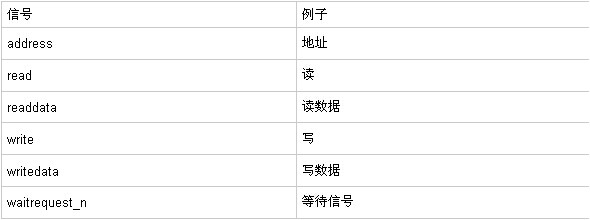
AVALON can therefore be said to be the simplest and most practical bus form. For its operation, the bus is a synchronous type bus. The write signal only needs to provide write data when the write enable is valid, and the read data is valid when the read data wait signal is invalid.
The width of the same data type read data (readdata) and write data (writedata) can be flexibly configured as (8, 16, 32----256---1024) BIT equivalent according to the design requirements. That is, it can support a very large bit width, but for a normal application, only (8, 16, 32, 64) BIT, etc. can be used to satisfy the application.
That assumes a bus width of 32, which is basically the width of the mainstream data bus. The byteenable signal is also necessary if a finer-grained partition is required to determine that a byte is valid. It requires 4 bits to indicate which one of the 32 bits (4 bytes) is valid, and each BIT represents one byte, so if all the bytes are to be fully valid, the width of the byte valid signal is (the width of the data bus / 8) . AVALON can also have a burst operation. The master device can determine the length of the brust by the burstcount device, which is an n-1 power of 2.
For normal applications, the basic operations in the above table can be used to meet the demand, which is the advantage of the AVALON-mm bus. In addition, the module provides a connection interface according to this standard, and various modules can be hung on the NIOSII system on chip.
If the modules are connected point-to-point and pass large amounts of data at the same time, the AVALON-mm bus is not suitable, so the AVALON_streaming bus is suitable for this application scenario.
The AVALON_streaming bus is essentially a synchronous parallel bus, that is, in the synchronous clock state, enabling the effective representation of the data transfer is valid. The basic signals are shown in the following table:
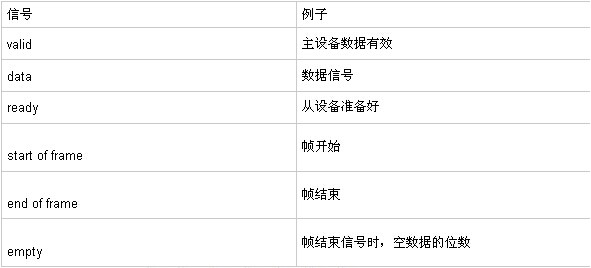
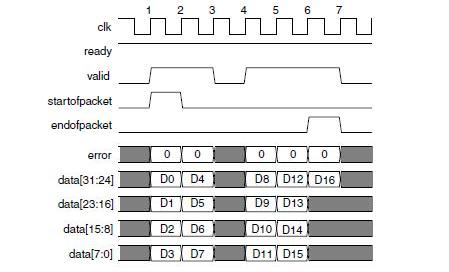
From the above figure, we can see the role of each signal in data transmission. For the processing of acquiring data from the device, when the VALID is valid, the data is effectively sampled, which is very simple and convenient and easy to handle. If the slave device setting ready is always 1, it means that there is no back pressure mechanism, then the master device can always send data packets to the slave device according to its own packet collection situation. There are also other auxiliary signals that can be added as needed for your design.
Use the bus to standardize the module for easy code migration and design reuse. At the same time, the setting and unified definition of the standard bus is also conducive to the standardization of the project team code, easy to understand and spread.
In the following, we will introduce two other bus types that are widely used. AHB (AMBA) If you are in the PC era, the monopoly of PCs is WINTEL (Microsoft and Intel), then in the era of mobile Internet, the most potential is Google’s andriod. Operating system and ARM chip. ARM-based ARM processors are basically monopolized in various types of embedded terminal devices. "The back of the tree is good for the cool", therefore, the AMBA bus standard used for ARM system processing for on-chip system interconnection has become the most widely used standard in the industry.
Jinhu Weibao Trading Co., Ltd , https://www.weibaoe-cigarette.com