Several wireless charging solutions features and schematics
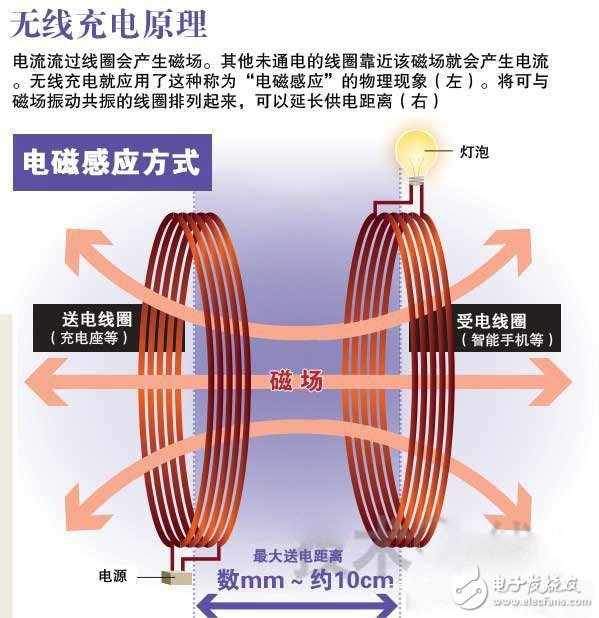
The development of wireless charging technology has been deeply researched and applied in the field of electronics. Although it has not been widely popularized, the development in the field of consumer electronics has achieved good results. Mobile phone manufacturers have also added this innovative advanced charging technology to their flagship machines, such as Samsung S6, Sony Xperia Z3+, Google Nexus 6, Nokia Lumia 930 and other mobile phones using wireless charging technology. So, what will happen to the future of wireless charging technology? What are the common wireless charging solutions now? Let's take a look at it:
1. Wireless Charging Alliance (WPC): Electromagnetic induction method, established in December 2008.
Currently, WIC's QI standard in commercial promotion currently has 172 member companies: Texas Instruments, Philips, Freescale, Toshiba, Microsoft, Panasonic, Samsung, Sony, and Qualcomm (last joined). and many more.
The wireless charging standard Qi developed by the Wireless Charging Alliance (WPC) uses electromagnetic induction. However, this technology has many defects. For example, the maximum output power is only 5W, so the charging speed will be very limited.
From the market scale, Qi is undoubtedly the most popular at present. It is worth noting that Qi's latest standard can achieve a wireless charging distance of 7 to 45 mm, which is a small breakthrough.
Advantages and disadvantages of electromagnetic induction technology adopted by QI labeling:
Advantages: simple principle, easy to make
Disadvantages: Transmission distance is severely limited
Examples are as follows:
1. Texas Instruments (TI): the earliest mass production wireless charging solution company
The first: Texas Instruments (TI), one of the major WPC members, has introduced the industry's first wireless power transmission control chipset. The set consists of a bq500110 single-channel transmit control chip and a bq51013 single-channel receive control chip. TI is the first mass production wireless charging solution company.

Second:
1, 15V input transmitter:
(1) Function description:
Second generation digital wireless power control transmitter
Used for charging portable devices such as mobile phones
Input 5V DC, output 10V AC
Look for WPC compatible devices that will be powered
Receive packet communication from powered devices and manage power transfer
(2) Important features:
Dynamic Power Limit (DPL)
5V operation in accordance with Wireless Power Consortium (WPC) Type A5 and Type A11 Transmitter Specifications
Digital demodulation reduces components
Integrated charge status mode and fault indication
(3) Functional block diagram:
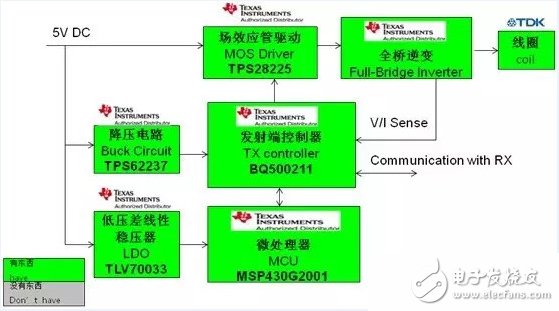
(4) Scheme photo:

2, 12V input transmitter:
(1) Function description:
TI Free Positioning Wireless Charging Transmitter
Apply to WPC 1.1 available phones, car and desktop charging
Three coils send array: Charging area > 70 mm × 20 mm
12V DC input, 5V AC output
Intelligent control of wireless power transmission
(2) Important features:
Compliant with Wireless Power Consortium (WPC) A6 Transmitter Specifications
Foreign object detection
Enhanced parasitic metal detection ensures safety
Digital demodulation
Overcurrent protection
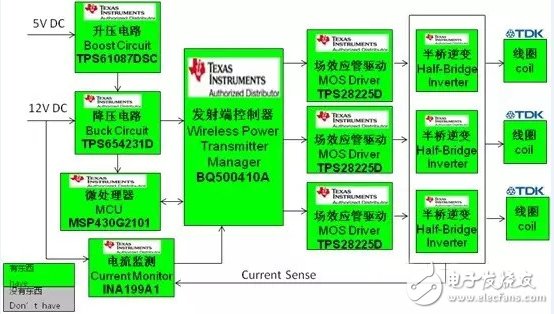
(3) Functional block diagram:
(4) Scheme photo:

3, 5V output receiver
(1) Function description:
Wireless power transmission receiver
Provide 5V regulated power supply output
Applied to portable devices for wireless charging
(2) Important features:
93% overall peak AC-DC efficiency
Communication control conforming to WPC v1.1 standard
Output voltage regulation
Internal Integrated Rectifier, Low-Voltage Buck Regulator, Digital Control
Thermal shutdown
(3) Functional block diagram:
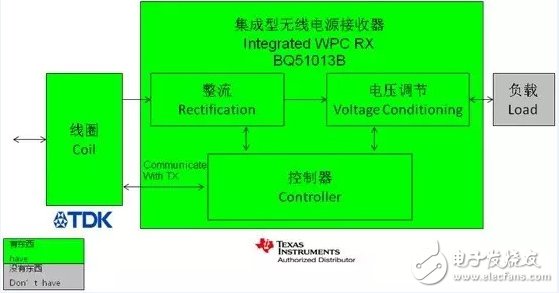
(4) Scheme photo:

2, Freescale (Highscale) efficient positioning wireless charging solution
5V input transmitter:
(1) Function description:
Free positioning charging device
Apply to WPC Qi available mobile phones, car and desktop charging
Provide accurate and efficient charging current
Adjustable input voltage
(2) Important features:
Compliant with WPC specifications
Efficient PID control loop with software platform using DSC core technology
Input voltage range 9~18 V
(3) Functional block diagram:
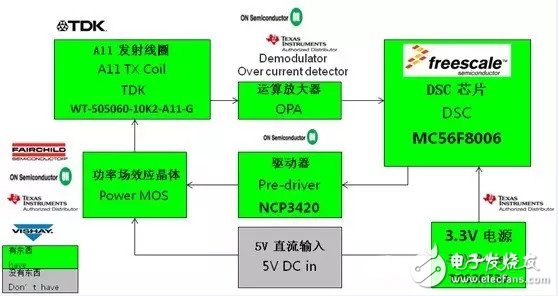
(4) Scheme photo:

3, Toshiba (Toshiba) simple fast wireless charging solution
5V output receiver:
(1) Function description:
Wireless charging receiver based on TC7761WBG
Battery block for smartphones, tablets
Compliant with WPC 1.1 protocol
(2) Important features:
Full bridge rectifier circuit
Undervoltage lockout / overvoltage protection
Maximum output voltage / current: 5V / 1A
Thermal shutdown detection and protection
(3) Functional block diagram:
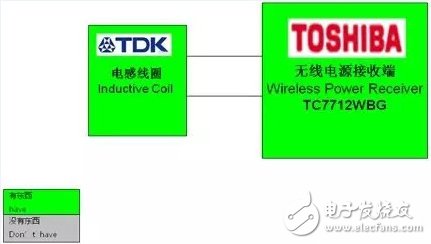
(4) Scheme photo:

4, Lingyang: Lingyang wireless charging chip GPM8F3132A
GPM8F3132A The first wireless charging chip that Lingyang Company fell out of is packaged in LQFP44 with a maximum power of 75%. It is the most versatile in terms of superior performance and cost performance.
Second, A4WP (Wireless Energy Alliance): Magnetic Resonance, established in May 2012
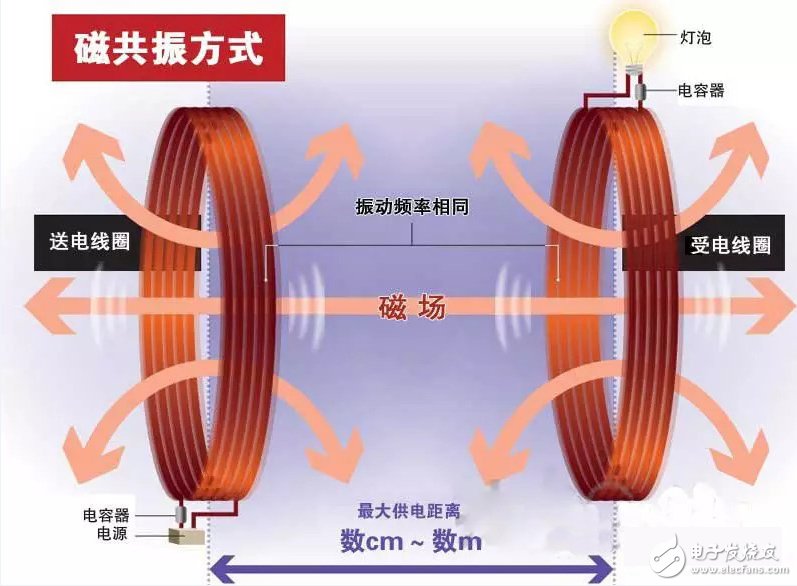
The A4WP (Wireless Energy Alliance), founded by Samsung and Qualcomm, currently has more than 40 members: Samsung, Qualcomm, Broadcom, Gill Industries, Integrated Device Technology (IDT), Intel, and more.
A4WP (Wireless Energy Alliance) wireless charging technology called "Rezence", using magnetic resonance (resonance sensing, also known as resonant coupling technology), although occasionally appeared in some electronic consumer exhibitions, but still not officially commercial.
Advantages and disadvantages of magnetic resonance technology used in A4WP:
Advantages: long transmission distance and high efficiency
Disadvantages: circuit frequency is not easy
Examples are as follows:
1, Intel Intel
(1) 2015 CES Asia Intel and Haier cooperate to push wireless charging solutions.
(2) On the second day of IDF 2015, Intel mentioned a cliché technology - wireless charging. Although this is not the first time Intel has applied the technology, but unlike the past, this Intel announced that it will Using the wireless charging function integrated in the sixth-generation Core processor "Skylake" released in the second half of the year, like the use of Centrino platform to promote wireless Internet access 12 years ago, to promote the popularity of wireless charging.
2, IDT company
IDT Corporation (Integrated Device Technology, Inc.) is working on a resonant transmitter-based integrated transmitter and receiver chipset for Intel's wireless charging technology. With IDT's leading technology, Intel is committed to providing verification reference designs for ultrabooks, all-in-ones, smartphones and stand-alone chargers.
3. American Witricity Corporation
Witricity also uses magnetic resonance to transmit electricity, and the transmission distance can reach several meters. MIT has used resonant sensing technology to increase the effective range of wireless charging to about two meters. The technology was named "WiTricity," and one of the researchers left the company and developed a system, but the price was more expensive. , reached 995 US dollars (about 6240 yuan).
Third, PMA (Power Union): electromagnetic induction
PMA, founded by Procter & Gamble and Powermat Technologies, has more than 70 members: it includes many communications and mobile phone manufacturers such as Samsung, Broadcom, HTC, LG and Huawei.
PMA (Power Alliance) is also using electromagnetic induction technology, which is later than WPC. Although PMA products can be found in the market, there are only a few, the largest commercial activities are supported by Starbucks, and free in some branches of the country. Wireless charging service, but the response is flat. On the other hand, it is already the fastest wireless charging standard in North America, and its distinctive feature is more biased towards charging devices, such as tables, furniture and so on.
It is worth noting that the two camps of A4WP and PMA also announced a formal merger. In the future, the two will focus on integrating magnetic resonance and magnetic induction technologies to promote the unification of wireless charging standards.
Fourth, WiFi wireless charging: 10 meters distance
Advantages: With the charge, it meets the concept of wireless charging
Disadvantages: charging object positioning is not easy, waste of power

The University of Washington has successfully developed a technology that uses Wi-Fi networks to charge hardware devices. It has successfully charged devices such as digital cameras within a Wi-Fi coverage distance of about 10 meters. The future is expected to charge the phone.
Wi-Fi networks are almost everywhere, and the purpose of the University of Washington R&D team is to use Wi-Fi routers as wireless charging devices to charge devices such as smartphones. This will solve the user's real problem more than the current wireless charging technology.
The university has developed a so-called "Wi-Fi power system." The system consists of two main components, one is a Wi-Fi access point (router) and the other is a custom charging sensor.
The project's researcher, Vamsi Talla, said that a charging sensor mounted on a hardware device is designed to receive electrical energy from a radio frequency signal (RF) and convert it to direct current for charging.
The team has developed a software solution that allows the Wi-Fi router to become a power supply, while at the same time acting as a data transfer role for traditional routers.
It should be pointed out that this Wi-Fi charging technology does not need to replace the traditional wireless router, only need to deploy software and other solutions, and after providing the charging function, it does not affect the function of the Internet access.
According to US reporters, Energous Inc. of the United States has introduced a device that uses radio frequency signals to provide power in the air. This device will no longer function as a Wi-Fi router when charging.
The University of Washington's new technology allows Wi-Fi networks to simultaneously transmit power and data. More precisely, this technology utilizes radio waves in Wi-Fi data transmission to transmit power.
According to reports, the research team at the University of Washington has found clever solutions that allow Wi-Fi networks to transmit data and transmit power without interfering with each other.
The "Connected" website commented that although the current Wi-Fi charging technology can only charge the device in the form of "small water flow" rather than "flowing flood", it is still an amazing achievement. As technology matures, future mobile phone and consumer electronics users may be able to forget the concepts of charging interface, charging cable, etc., only need to use Wi-Fi network to charge.
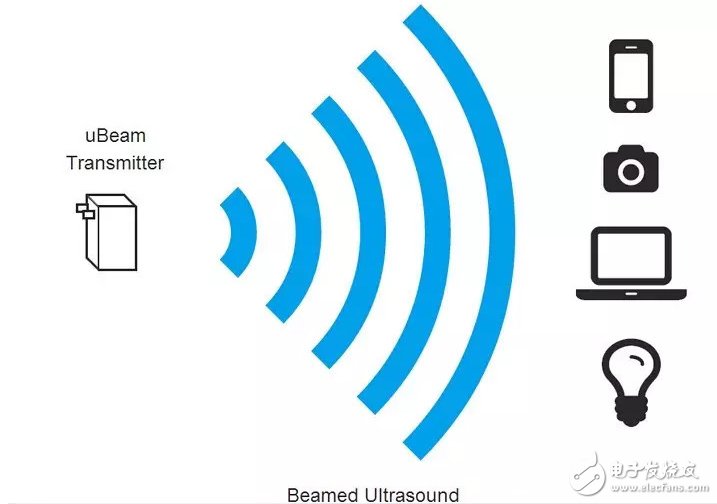
Five, ultrasonic wireless charging: effective range is close to 5 meters
Advantages: The technology is very safe; the receiver is cheap and small; it can be used for data transmission.
Disadvantages: The final product may not meet expectations in terms of price, power, speed and safety.
A company called uBeam invented a new wireless charging mode that uses ultrasound to transport power to a distance of 15 feet (about 4.6 meters). With such a product, you can use your mobile phone to move around the house while charging while using a dedicated wireless charging kit.
This technology was thought of by a 25-year-old New York girl, Meredith Perry. uBeam has received $1.7 million in seed round financing, including Yahoo CEO Marissa Mayer, Founders Fund and Andreessen Horowitz. The company has applied for 18 patents related to wireless charging and ultrasound.
Sixth, Microsoft intends to use focused light to charge
Microsoft Research has developed a potential solution: AutoCharge. Microsoft researchers describe AutoCharge as a technology that automatically locates and charges computers on their desks. The prototype charger they built can be mounted on the ceiling and has two working modules: a monitoring module that uses Microsoft's Kinect camera to scan objects like smartphones; the other is charging mode, using UltraFire CREE XM-L T6 to focus LED light.
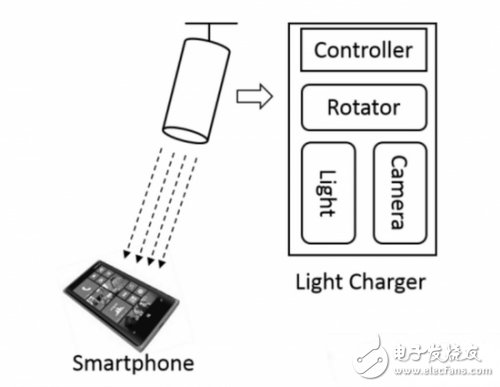
The AutoCharge system uses image-based processing to monitor and track smartphones on the table and automatically charge smartphones. The charger will continue to rotate until it detects an object that looks like a smartphone, and then uses the beam generated by solar power technology to remotely charge the smartphone. In other words, no wires are needed.
To learn more about wireless charging solutions, check out the following related articles and posts:
1. Analysis of wireless charging principle and collection of classic design schemes
2. [Recommended] Wireless charging principle and solution technology topic
3. Simple wireless charging system DIY design
4. Smart wearable device wireless charging reception solution diagram
5. Wireless charging solution based on TI and Toshiba
6. Wearable device wireless charging solution with iBeacon function
7. Active-Semi pushes low-cost Qi Certified wireless charging IC solution
Live broadcast: IDT big coffee clock Yingdong teaches you how to quickly get consumer electronics wireless charging design
Register now->>

Activities: Participate in the IDT Wireless Charging Application Design Competition, grab the precious metal smart watch
Join now->>

High Temperature Heat-Shrinkable Tube
KYNAR HEAT SHRINKABLE TUBE/PVDF Heat Shrinkable Tube
Product description:
KY-175℃ KYNAR Heat Shrinkable Tube / Bicycle brake wireis protected Heat Shrinkable sleeving made of irradiation cross-linked special fluorine polymer PVDF ( polyvinylidene fluoride ). PVDF Heat-Shrinkable tube with the specialty of superior chemical and physical properties, high temperature resistance, high flame resistance, chemical solvent resistance, rub resistance, and so on.
KY-175 ℃ KYNAR Heat-shrinkable tubing for automobile stay wire /Friction-resistant heat-shrinkable tube it`s used in Automobile, Car,Electronics, Military, Medical equipment and other fields and allies to industries: automobile, motorcycle cables,bicycle brake cables for insulation protection. Scalpel,coagulator knife, electric coagulation knife and other metal medical equipment for insulation protection.
Feature & benefit:
a) Semi-hard materials, thin wall design
b) Resistant to 175 degrees Celsius
c) Shrink ratio: 2/1, 3/1
d) High flame resistance VW-1
e) Transparent design, inner player is visual when operating
Operating Indexes:
a) Min. Shrink temp.: 155 degrees Celsius
b) Recovered Shrink temp.: 175 degrees Celsius
c) Working temperature: -55~175 degrees Celsius
Up to standard: Approvals
Meet AMS-DTL-23053/18 , Class 2
Meet UL224 150 degrees Celsius 600V VW-1
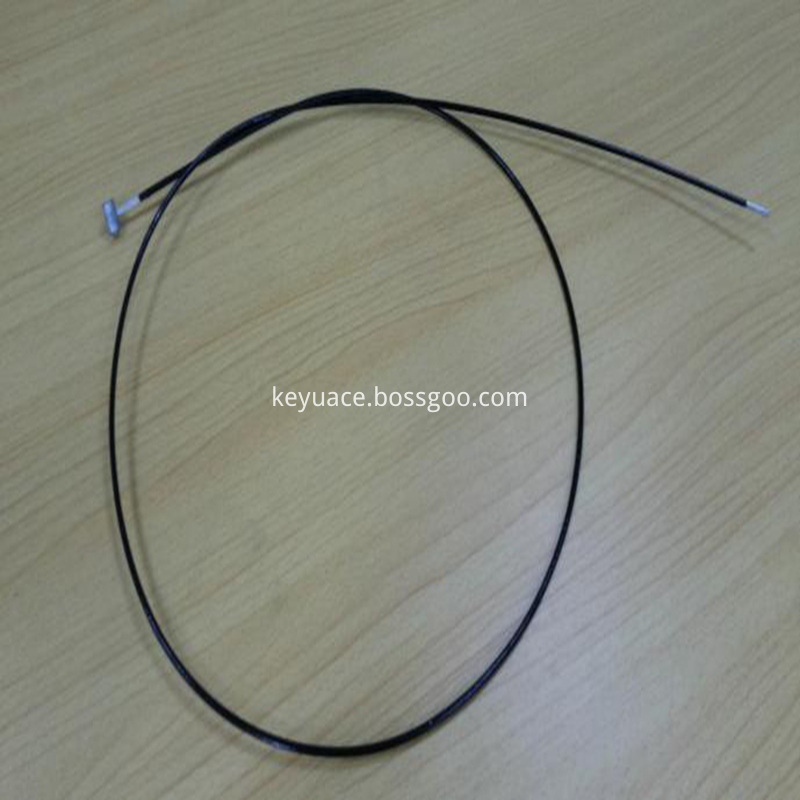
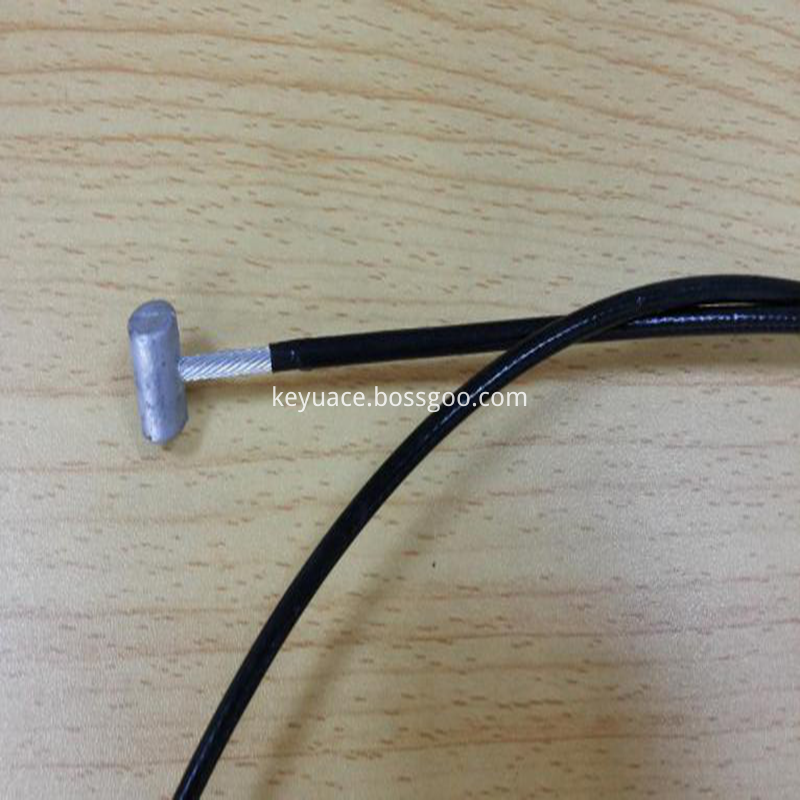






Friction resistant heat shrinkable tube,KYNAR HEAT SHRINKABLE TUBE,PVDF Heat Shrinkable Tube,The brake line protects the heat-shrinkable tube
KEYUACE Materials Co., Ltd. , https://www.insulationtubing.com