Discussion on the planning and design of IP bearer network
Undoubtedly, the development of modern communication networks is determined by business needs and market demands, not the development of technology. Let ’s look back at the development of the Internet (IP network), and the traces of market promotion are very obvious: this kind of IP network technology that was born in the 60s and 70s was only developed rapidly in the late 1990s. In the late 20th century, file sharing, e-mail, network computing, and web browsing and other business needs worked together.
Similarly, the requirements of the 3G system for IP bearer networks are also determined by their business needs. According to statistics, in China, mobile data communications business revenue accounts for about 15% of the entire mobile communications industry. From this proportion, it is clear that the real revenue generation is still the voice business. Even in economically developed Europe, in countries that have already opened 3G services, voice services still account for as much as 85%.
Therefore, it can be believed that the 3G business in the next 5 years should be in such a pattern: with voice business as the leading factor, data business is developing rapidly. Whether it is a 3G wireless network or an IP bearer network design, this factor must be considered.
In response to this feature, we need to analyze the traffic models of voice services and data services:
The voice traffic model is different from the traffic model of general Internet data services. Voice traffic is basically symmetrical, and the difference between upstream and downstream is very small, and the upstream and downstream traffic of each Internet business flow is different. In addition, its requirements for service quality are also different. Whether it is voice or video, these real-time services are very sensitive to the delay and jitter of data packets, and they are very demanding on QOS; while Internet HTTP, FTP, e-mail, etc. There are no special requirements for services, as long as the data packets arrive before the timeout.
From the perspective of safety and reliability, the requirements of the two are also different. Since voice communication has become an indispensable tool for people's life and work, even if the telephone traffic is carried on the IP network, its original reliability must also be guaranteed; and Internet web browsing, online games and other services are far from essential. the height of.
These business characteristics determine the particularity of the 3G IP bearer network: on the one hand, it is necessary to ensure the reliability and security of traditional voice services, after all, this is the main source of business revenue; on the other hand, it also needs to provide multiple services (such as video, image, data Etc.), this is the direction of future development! Neither of them should be disregarded.
Network isolation
Based on the different needs of 3G services, the industry has basically reached the principle that the 3G IP bearer network is isolated from the traditional Internet network, whether it is logically or physically isolated.
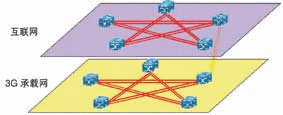
Figure 1 Schematic diagram of network isolation
At present, Chinese operators already have one or more IP networks: such as China Telecom's 163, China Netcom's 169 and mobile CMNET. The largest of these are generally IP networks that carry out Internet services. In this case, the construction of the 3G bearer network will encounter this question: rebuild the existing network or create a new private network?
In fact, the industry has never lacked such a similar argument. The core of the argument is nothing more than investment costs and management costs. However, let's look at the final result. China Mobile has built an IP private network outside CMNET, and China Telecom has completed the deployment of the new CN2. Therefore, practice has proved that the most frugal and effective solution is to build another physical private network.
Renovating the existing network is nothing more than upgrading equipment capabilities and expanding line capacity on the basis of the current, and then using corresponding VPN technology to logically isolate 3G services. In terms of investment costs, the cost of upgrading old equipment and lines, and the cutover of old networks is not low. Moreover, if the reconstructed 3G service and the Internet service share a physical network, there will be big problems: Due to the explosive growth of Internet services, its demand for bandwidth is difficult to predict, and it is likely to cause network congestion in the short term, repeated expansion, and finally need to build a new network, causing greater waste. While 3G services are currently dominated by voice, their traffic models are very different from Internet services, and are not suitable for sharing a link bandwidth. In the long run, the new network will save more investment.
Second, the opening of the 3G bearer network on the basis of the existing network will also bring a sharp increase in management costs. Due to the introduction of VPN technology, it obviously brings network complexity. Difficulties in network management and service provisioning increase, and various complex routing strategies, VPN, QOS and other technologies are required to isolate and coordinate 3G services and other services, so that 3G MSC, signaling gateways and media gateways and other equipment can be used with many existing networks Internet servers, gateways and terminals work safely on the same physical network.
Third, the physical isolation of the Internet can prevent the Internet from causing security problems. Due to the increasing scale and users of the Internet, the Internet has evolved into a very open, free, and very complex communication method. There is a lack of reasonable control in this network and it is full of conflicts, viruses and anti-viruses, confidentiality and interception, sharing and copyright protection. Once there is a network attack, the network is paralyzed, even the logically isolated 3G bearer network is not immune, after all, they run together on a physical device. Moreover, with the development of the Internet today, security has always been an important and existing problem.
As the cost of IP network equipment decreases, the future 3G bearer network should and can be built on a new IP network. It is currently not suitable for coexistence with the Internet in the same network.
In fact, in the specific business bearer strategy, 3G services will operate on its IP dedicated bearer network and the Internet at the same time: 3G system signaling VPN, CS domain services (voice) and PS domain streaming media and other real-time services are all It can be carried on the IP dedicated bearer network; services such as web browsing, file sharing, and online games can be introduced to the Internet through the Gi interface. In this way, the aforementioned 3G service requirements can be met, and multiple physical networks can be fully utilized, which improves the operator's investment efficiency.
Network framework and site router
According to the current flat trend of network development, the future IP bearer network should minimize the network layer. According to the actual situation in China and the characteristics of 3G node deployment, there are generally two approaches: first, the national network is flattened to prefectures; second, the provincial network is flattened to all nodes in prefectures and cities. These two structures are generally in line with the principle of simplicity and efficiency for operators preparing to develop 3G services on a large scale.
Solution 1 (Figure 2): The national network is flattened to prefectures and cities, and provincial networks are no longer set up. The national backbone network is directly connected to the prefecture-city metropolitan area network; the prefecture-city metropolitan area network consists of 3G site routers (Site Router). Access 3G services.
Please refer to the picture below:
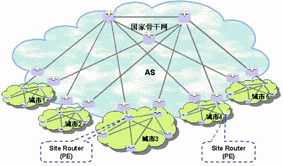
Figure 2 Network framework one
This method of pushing the edge of the national backbone network to the boundary of the metropolitan area network has the main advantages of being convenient for centralized management and facilitating the opening of cross-provincial services. What needs to be mentioned is that this kind of network structure has a high requirement for the maintenance system, and a centralized maintenance technical team is needed for the entire network. For a network with hundreds of nodes and multiple services such as VPN, it needs to be relatively large. The maintenance, strategy optimization team. Therefore, this is not only a technical issue, but also a network management system issue, which requires operators to carefully consider.
Scheme 2 (Figure 3): Flatten the provincial network and deploy it to the 3G node (Site) of each prefecture. The main equipment of the provincial network is the 3G site router; the national backbone network remains The simple and clear network structure only involves one or two outlets in each province.
This kind of network can also achieve the purpose of flat network. The provincial department manages the entire IP bearer network, which facilitates the opening of services in the province. For the current Chinese operators, it does not involve large-scale management system changes. Therefore, this is a good choice.
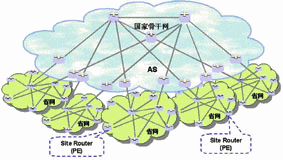
Figure 3 Network framework two
In the above scheme design, there is a very key place: that is the configuration of the 3G Site Router. This site router is mainly a bridge between the IP bearer network and the core equipment (MSC, MGW, etc.) in each 3G Site. It assumes the role of PE in VPN applications, whether in the bearer network or in the 3G core network. Possess a pivotal role.
Therefore, equipment providers will strictly screen their site routers, especially with 3G core network equipment for a full range of tests to ensure that it can complete its role as a bridge without compromise. Therefore, this site router is an indispensable basic device in each equipment provider's 3G Site solution. Directly adopt the site routers screened out by the 3G equipment providers. One is to ensure that the 3G network can be opened smoothly and quickly. After all, time is money, which is a practical problem faced by operators; 3G business.
In theory, all IP routers follow the standards of IETF and ITU, and there should be no problem in replacing each other. But the facts tell us that there are still incompatibilities in the equipment of different manufacturers. In fact, this is not to be blamed. If all manufacturers use the same mold to produce products, wouldn't the whole world be very monotonous and boring? At the same time, because site routers will face multiple devices in the 3G core network at the same time, each device may have some special requirements for it, so the selection of these routers is very strict. The incompatibility of IP routers with certain soft-switching devices is actually a common occurrence in many projects.
The more practical approach is of course to configure the site routers of the 3G equipment provider, and at the same time combine some site routers and some aggregation routers to form a concise and efficient 3G bearer network (metropolitan area network or provincial network). As shown below (Figure 4):
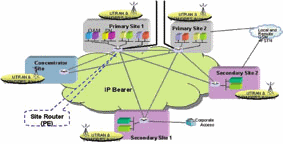
Figure 4 Site router network
This metropolitan area network or provincial network, combined with the national backbone network, is an ideal, flat 3G IP bearer network. However, in some design schemes, a group of routers were added as a 3G PE device in front of these site routers (Site Router), the entire network structure immediately became very complicated, weakening the role of network flattening, and It also wastes investment.
Conclusion
Regarding the 3G IP bearer network, the above views and ideas are summed up in actual work, and may be biased. I hope everyone can consider together.
Similarly, the requirements of the 3G system for IP bearer networks are also determined by their business needs. According to statistics, in China, mobile data communications business revenue accounts for about 15% of the entire mobile communications industry. From this proportion, it is clear that the real revenue generation is still the voice business. Even in economically developed Europe, in countries that have already opened 3G services, voice services still account for as much as 85%.
Therefore, it can be believed that the 3G business in the next 5 years should be in such a pattern: with voice business as the leading factor, data business is developing rapidly. Whether it is a 3G wireless network or an IP bearer network design, this factor must be considered.
In response to this feature, we need to analyze the traffic models of voice services and data services:
The voice traffic model is different from the traffic model of general Internet data services. Voice traffic is basically symmetrical, and the difference between upstream and downstream is very small, and the upstream and downstream traffic of each Internet business flow is different. In addition, its requirements for service quality are also different. Whether it is voice or video, these real-time services are very sensitive to the delay and jitter of data packets, and they are very demanding on QOS; while Internet HTTP, FTP, e-mail, etc. There are no special requirements for services, as long as the data packets arrive before the timeout.
From the perspective of safety and reliability, the requirements of the two are also different. Since voice communication has become an indispensable tool for people's life and work, even if the telephone traffic is carried on the IP network, its original reliability must also be guaranteed; and Internet web browsing, online games and other services are far from essential. the height of.
These business characteristics determine the particularity of the 3G IP bearer network: on the one hand, it is necessary to ensure the reliability and security of traditional voice services, after all, this is the main source of business revenue; on the other hand, it also needs to provide multiple services (such as video, image, data Etc.), this is the direction of future development! Neither of them should be disregarded.
Network isolation
Based on the different needs of 3G services, the industry has basically reached the principle that the 3G IP bearer network is isolated from the traditional Internet network, whether it is logically or physically isolated.

Figure 1 Schematic diagram of network isolation
At present, Chinese operators already have one or more IP networks: such as China Telecom's 163, China Netcom's 169 and mobile CMNET. The largest of these are generally IP networks that carry out Internet services. In this case, the construction of the 3G bearer network will encounter this question: rebuild the existing network or create a new private network?
In fact, the industry has never lacked such a similar argument. The core of the argument is nothing more than investment costs and management costs. However, let's look at the final result. China Mobile has built an IP private network outside CMNET, and China Telecom has completed the deployment of the new CN2. Therefore, practice has proved that the most frugal and effective solution is to build another physical private network.
Renovating the existing network is nothing more than upgrading equipment capabilities and expanding line capacity on the basis of the current, and then using corresponding VPN technology to logically isolate 3G services. In terms of investment costs, the cost of upgrading old equipment and lines, and the cutover of old networks is not low. Moreover, if the reconstructed 3G service and the Internet service share a physical network, there will be big problems: Due to the explosive growth of Internet services, its demand for bandwidth is difficult to predict, and it is likely to cause network congestion in the short term, repeated expansion, and finally need to build a new network, causing greater waste. While 3G services are currently dominated by voice, their traffic models are very different from Internet services, and are not suitable for sharing a link bandwidth. In the long run, the new network will save more investment.
Second, the opening of the 3G bearer network on the basis of the existing network will also bring a sharp increase in management costs. Due to the introduction of VPN technology, it obviously brings network complexity. Difficulties in network management and service provisioning increase, and various complex routing strategies, VPN, QOS and other technologies are required to isolate and coordinate 3G services and other services, so that 3G MSC, signaling gateways and media gateways and other equipment can be used with many existing networks Internet servers, gateways and terminals work safely on the same physical network.
Third, the physical isolation of the Internet can prevent the Internet from causing security problems. Due to the increasing scale and users of the Internet, the Internet has evolved into a very open, free, and very complex communication method. There is a lack of reasonable control in this network and it is full of conflicts, viruses and anti-viruses, confidentiality and interception, sharing and copyright protection. Once there is a network attack, the network is paralyzed, even the logically isolated 3G bearer network is not immune, after all, they run together on a physical device. Moreover, with the development of the Internet today, security has always been an important and existing problem.
As the cost of IP network equipment decreases, the future 3G bearer network should and can be built on a new IP network. It is currently not suitable for coexistence with the Internet in the same network.
In fact, in the specific business bearer strategy, 3G services will operate on its IP dedicated bearer network and the Internet at the same time: 3G system signaling VPN, CS domain services (voice) and PS domain streaming media and other real-time services are all It can be carried on the IP dedicated bearer network; services such as web browsing, file sharing, and online games can be introduced to the Internet through the Gi interface. In this way, the aforementioned 3G service requirements can be met, and multiple physical networks can be fully utilized, which improves the operator's investment efficiency.
Network framework and site router
According to the current flat trend of network development, the future IP bearer network should minimize the network layer. According to the actual situation in China and the characteristics of 3G node deployment, there are generally two approaches: first, the national network is flattened to prefectures; second, the provincial network is flattened to all nodes in prefectures and cities. These two structures are generally in line with the principle of simplicity and efficiency for operators preparing to develop 3G services on a large scale.
Solution 1 (Figure 2): The national network is flattened to prefectures and cities, and provincial networks are no longer set up. The national backbone network is directly connected to the prefecture-city metropolitan area network; the prefecture-city metropolitan area network consists of 3G site routers (Site Router). Access 3G services.
Please refer to the picture below:

Figure 2 Network framework one
This method of pushing the edge of the national backbone network to the boundary of the metropolitan area network has the main advantages of being convenient for centralized management and facilitating the opening of cross-provincial services. What needs to be mentioned is that this kind of network structure has a high requirement for the maintenance system, and a centralized maintenance technical team is needed for the entire network. For a network with hundreds of nodes and multiple services such as VPN, it needs to be relatively large. The maintenance, strategy optimization team. Therefore, this is not only a technical issue, but also a network management system issue, which requires operators to carefully consider.
Scheme 2 (Figure 3): Flatten the provincial network and deploy it to the 3G node (Site) of each prefecture. The main equipment of the provincial network is the 3G site router; the national backbone network remains The simple and clear network structure only involves one or two outlets in each province.
This kind of network can also achieve the purpose of flat network. The provincial department manages the entire IP bearer network, which facilitates the opening of services in the province. For the current Chinese operators, it does not involve large-scale management system changes. Therefore, this is a good choice.

Figure 3 Network framework two
In the above scheme design, there is a very key place: that is the configuration of the 3G Site Router. This site router is mainly a bridge between the IP bearer network and the core equipment (MSC, MGW, etc.) in each 3G Site. It assumes the role of PE in VPN applications, whether in the bearer network or in the 3G core network. Possess a pivotal role.
Therefore, equipment providers will strictly screen their site routers, especially with 3G core network equipment for a full range of tests to ensure that it can complete its role as a bridge without compromise. Therefore, this site router is an indispensable basic device in each equipment provider's 3G Site solution. Directly adopt the site routers screened out by the 3G equipment providers. One is to ensure that the 3G network can be opened smoothly and quickly. After all, time is money, which is a practical problem faced by operators; 3G business.
In theory, all IP routers follow the standards of IETF and ITU, and there should be no problem in replacing each other. But the facts tell us that there are still incompatibilities in the equipment of different manufacturers. In fact, this is not to be blamed. If all manufacturers use the same mold to produce products, wouldn't the whole world be very monotonous and boring? At the same time, because site routers will face multiple devices in the 3G core network at the same time, each device may have some special requirements for it, so the selection of these routers is very strict. The incompatibility of IP routers with certain soft-switching devices is actually a common occurrence in many projects.
The more practical approach is of course to configure the site routers of the 3G equipment provider, and at the same time combine some site routers and some aggregation routers to form a concise and efficient 3G bearer network (metropolitan area network or provincial network). As shown below (Figure 4):

Figure 4 Site router network
This metropolitan area network or provincial network, combined with the national backbone network, is an ideal, flat 3G IP bearer network. However, in some design schemes, a group of routers were added as a 3G PE device in front of these site routers (Site Router), the entire network structure immediately became very complicated, weakening the role of network flattening, and It also wastes investment.
Conclusion
Regarding the 3G IP bearer network, the above views and ideas are summed up in actual work, and may be biased. I hope everyone can consider together.
Sound Bar,Rgb Light Sound Bar,Gaming Sound Bar,Hifi Soundbar Speaker,Echo Wall
Comcn Electronics Limited , https://www.comencnspeaker.com