Hydraulic brake Bosch solution for braking energy recovery in automotive electronics
Brake energy recovery, for an electrically driven vehicle, means that during deceleration or braking, the drive motor operates in a power generation state, and converts part of the kinetic energy of the vehicle into electrical energy for storage in the battery. At the same time, the motor is fed back to the drive shaft to brake the vehicle. This type of braking is called regenerative braking (RegeneraTIve Braking) or feedback braking. The application of braking energy recovery technology in electric drive vehicles can increase the cruising range of the vehicle at one charge.
Brake energy recovery is done by an electric brake system and a hydraulic brake system. The hydraulic brake system is the key actuator of the brake energy recovery system. Its task is to control the brake pressure to ensure the driver's good brake pedal feel and ensure the safety of the whole vehicle brake. The hydraulic brake system of the electric vehicle brake energy recovery system is different from the brake system of the traditional fuel vehicle. On the one hand, the electric vehicle does not have the traditional internal combustion engine to provide the vacuum system for the brake system, and the other is the brake energy recovery. Implementation requires a signal exchange between the hydraulic brake system and the motor.
Based on the technical requirements of the regenerative braking system, major automobile manufacturers and component companies have introduced hydraulic brake system solutions with different braking energy recovery functions for different types of electric drive vehicles. Next, let's talk about several typical solutions in the industry.
1. Vacuum assisted hydraulic brake system
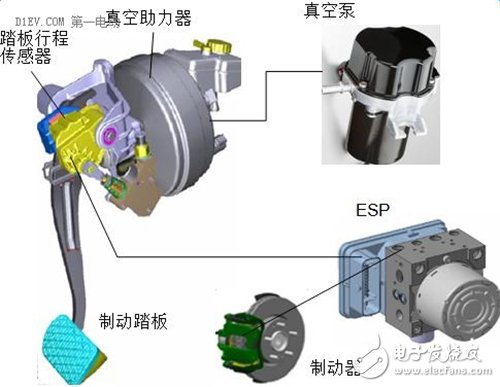
"Vacuum booster + vacuum pump" program
The solution is mainly to add EVP (Electronics Vacum Pump), PTS (Pedal Travel Sensor) and air pressure sensor to the original vacuum assisted hydraulic brake system.
The role of the EVP is to provide a power source for the vacuum booster because the electric drive passenger car does not have a conventional engine and cannot provide vacuum for the vacuum booster. The vacuum booster cannot provide brake boost without vacuum. The system usually also has a vacuum tank for storing a certain volume of vacuum, which makes the system's vacuum more stable, while reducing the frequency of EVP startup and increasing the life of the EVP. PTS is mainly used to provide braking signals to the motor controller, effectively utilizing the brake idle travel for energy recovery and improve energy recovery.
The advantage of this system is that most of the components of the original braking system can be used, the implementation is convenient, the technology is mature, the system is stable, and the cost is low. The disadvantage is that the motor feedback braking force is directly superimposed on the original friction braking force, the original friction braking force is not adjusted, the energy recovery rate is low, and the braking comfort is poor. The poor braking comfort is not only the impact and smoothness of the coupling and switching of the motor feedback brake and the friction brake, but also in the plateau area. Due to the low air pressure, the EVP cannot provide the same high vacuum as in the plain area. The booster of the vacuum booster is poor and the pedal force is increased.
2. ESP/ESC based hydraulic brake system
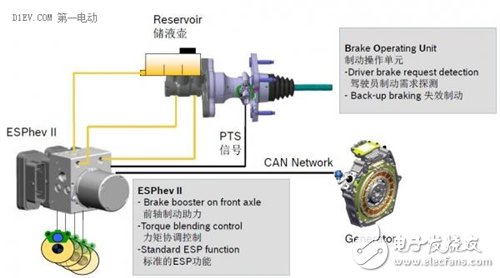
Bosch ESPhev solution
Take Bosch's ESPhev as an example. The system does not require a vacuum booster and EVP. It is based on the original ESP technology. In addition to the standard functions, ESP adds the conventional brake hydraulic assist function and feedback torque coordination function. The ESP calculates the driver's braking demand based on the PTS signal in the BOU (Brake Opera TIng Unit), and then distributes the braking force according to the amount of feedback braking force that the motor can provide and the stability of the integrated vehicle. Brake system pressure is provided by ESP.
The system has a smaller installation size than the conventional brake system, lighter weight, coordination of feedback torque and hydraulic torque, and high energy recovery. However, the front axle of the system is decoupled, and the brake pipe is a type II arrangement, which is different from the common X-type arrangement, and the scheme is only applicable to small cars (the full load does not exceed 1700kg).
3. EHB based hydraulic brake system
EHB (Electronics Hydraulic Brake), mainly composed of power unit (motor, pump and accumulator), hydraulic unit (master cylinder, pedal simulator and PTS) and electronic control unit, via brake line The control valve is connected to the brake wheel cylinder to control the brake fluid to flow into/out of the brake wheel cylinder, thereby achieving brake pressure control.
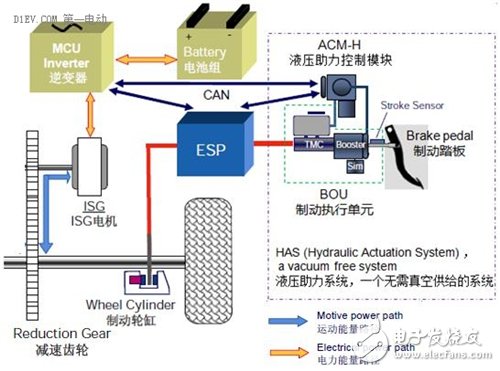
Bosch HAShev solution
The picture above shows Bosch's HAShev system, which consists mainly of BOU, ACM-H (ActuaTIon Control Module–Hydraulic, hydraulic assist control module) and ESP. The BOU is equipped with a PTS to detect the driver's braking demand; the BOU and the brake pedal are decoupled and integrated with a pedal feel simulator. The pedal feel simulator is mainly a spring damper mechanism that can flexibly adjust the pedal feel. The ACM-H is mainly composed of an electric hydraulic pump, a high-pressure accumulator and an electronic control unit. Its task is mainly to supply the hydraulic brake system and coordinate control of the feedback torque and hydraulic torque. Compared with the ordinary ESP, the ESP of the system has the function of active boosting. It can actively boost when the ACM-H fails, ensuring the safety of the brakes. At the same time, it also has feedback between the motor control unit and the ACM-H. Signal interactions such as torque and vehicle stability factor.
The pedal decoupling of the system can flexibly design the pedal feel, dynamically control the coordinated distribution of the motor feedback torque and the hydraulic braking torque, and preferentially utilize the regenerative torque to achieve the maximum efficiency of braking energy recovery; at the same time, it has a powerful failure mode, ACM- ESP can be compensated when H fails, and the mechanical structure is guaranteed to be safe when the hydraulic fails. However, the system has many components and complicated structures. It is necessary to add 4 brake pipes, which has no weight advantage and high debugging and maintenance costs.
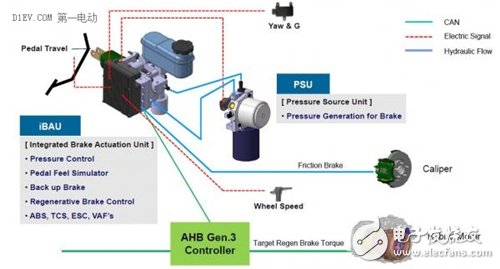
Mando AHBIII program
The picture above shows the AHBIII solution of Mando Company of South Korea. It consists of two main components: iBAU (Integrated Brake ActuaTIon Unit) and PSU (Pressure Source Unit). Compared with Bosch's HAShev system, Mando integrates the electronic control unit and ESP/ESC into the iBAU. The number of components is reduced, the layout is more flexible, the weight is lighter, and the weight is almost 2kg. Moreover, iBAU directly performs wheel pressure control to minimize system loss and enhance pressure controllability.
4. Hydraulic brake system based on new brake booster
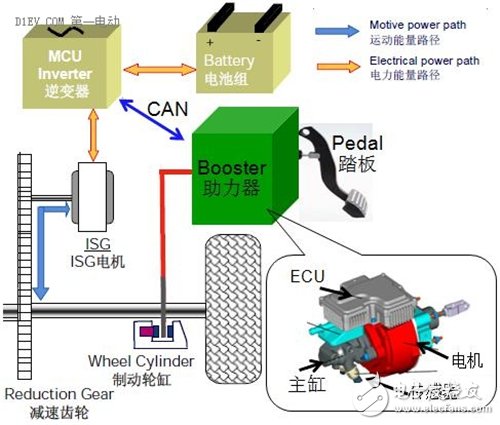
New brake booster based solution
This solution has no vacuum booster and EVP, nor a hydraulic pump or accumulator. Instead, a high-performance motor is used to drive the piston linearly through the gear mechanism to generate the brake master cylinder pressure. Compared with the ordinary brake system, it is lighter, the system responds faster, can significantly increase the building pressure speed, effectively shorten the braking distance, and meet the higher requirements of the new advanced driver assistance system for the dynamic characteristics of the brake pressure control. Coordinated regenerative braking functions are similar to those based on ESP/ESC and EHB technologies, as well as efficient braking energy recovery.
The brake pedal of the system can also be decoupled, and there is no direct connection between the pressure build process and the brake pedal, which is generated by a spring/buffer unit integrated in the actuator module. The pedal feel can be adjusted according to the requirements of the vehicle. It can also be adjusted according to different driving conditions (such as emergency braking) or operating mode (such as “sportsâ€). It can realize regenerative braking without any additional measures. The perfect unity of comfort.
This program has been successfully applied to Nissan Leaf, Tesla Model S and Alfa Romeo Giulia.

Continental Group's MKC1 (integrated with ESC)
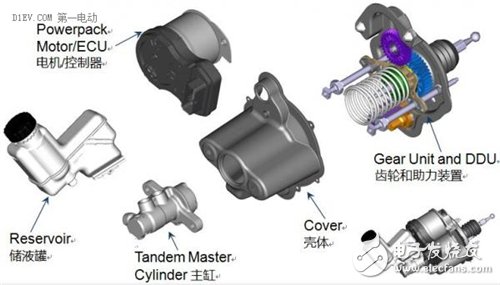
Bosch's ibooster (no integrated ESP/ESC)
Compared with traditional brake system products, the development cost of EHB or new brake booster is relatively high, but with the continuous advancement of technology, these development costs will continue to decrease. We believe that the brake system will gradually move towards lightweight, modular and intelligent EHB or new brake boosters. At present, major foreign brake system parts suppliers (such as Bosch, TRW, Continental, Adix, Hitachi, Wandu, etc.) have launched their own EHB or new brake booster products, and our domestic suppliers are due to There are shortcomings in the development and manufacture of key components such as ESP/ESC/EHB and solenoid valves in traditional chassis electronic control systems. There is still a gap between the development of EHB or new brake booster products and foreign countries. However, domestic research and development in this area has also made some progress, such as electro-hydraulic boosters, electronic vacuum boosters, etc., which have already formed products, and many domestic suppliers are working with some universities to achieve good results through industry-university-research cooperation. progress. With the gradual advancement of the industrialization process of electric vehicles, it is believed that domestic suppliers can also develop products such as EHB or new brake boosters that meet the needs of complete vehicles, and form the ability to compete with similar foreign standards.
Indoor Fixed LED Display is a popular product for its high quality, every year sold to at least 80,000 pieces around the world, including Europe, North America, southeast Asia.Compared to other indoor LED display in the market, its biggest advantage is that it can display high-definition images while maintaining low power consumption.Besides, it adopts Die casting aluminum cabinet which is ultra-thin and ultra-light and owns good heat dissipation.Easy to install and maintain and suitable for multiple indoor scenes.
Application:
* Business Organizations:
Supermarket, large-scale shopping malls, star-rated hotels, travel agencies
* Financial Organizations:
Banks, insurance companies, post offices, hospital, schools
* Public Places:
Subway, airports, stations, parks, exhibition halls, stadiums, museums, commercial buildings, meeting rooms
* Entertainments:
Movie theaters, clubs, stages.
Indoor Fixed LED Display,Led Wall Display,Video Wall Display,Outdoor Led Screen Display
Guangzhou Chengwen Photoelectric Technology co.,ltd , https://www.cwleddisplay.com