Read the difference between the Internet of Things and the Internet
Internet of Things (Internet of Things), as the name suggests, is "the Internet connected by objects"; it is an information-sensing device such as a radio frequency identification (RFID) device, an infrared sensor, a global positioning system, a laser scanner, etc., according to a contractual agreement. A network that connects to the Internet for information exchange and communication for intelligent identification, location, tracking, monitoring, and management.
The Internet of Things is a dynamic global network infrastructure with self-organizing capabilities based on standards and interoperable communication protocols, where physical and virtual "objects" have identities, physical attributes, virtual features, and intelligent interfaces. Seamless integration with information networks. The Internet of Things will work with the media Internet, the Internet of services and the corporate Internet to form the future of the Internet.
The Internet of Things is widely used in intelligent transportation, environmental protection, government work, public safety, safe home, intelligent fire protection, industrial monitoring, elderly care, personal health, flower cultivation, water system monitoring, food traceability, enemy investigation and intelligence gathering. field. Therefore, the Internet of Things technology is also known as the "Smart Earth" strategy.
The IoT industry chain includes eight major segments: chip providers, sensor suppliers, wireless module (including antenna) manufacturers, network operators, platform service providers, system and software developers, intelligent hardware vendors, system integration and application service providers.
Internet of Things Industry Chain(1) chip provider: the brain of the Internet of Things;
Low-power, high-reliability semiconductor chips are one of the key components that are essential in almost every aspect of the Internet of Things. Depending on the function of the chip, the chips required in the IoT industry include chips integrated into sensors and wireless modules to implement specific functions, as well as embedded microprocessors embedded in terminal devices to provide "brain" functions. Traditional international semiconductor giants such as ARM, Intel, Qualcomm, Freescale, etc.; major domestic manufacturers include: Huawei Hisilicon, Spreadtrum, Beijing Junzheng, Huatian Technology.
(2) Sensor supplier: shaping the five senses of the Internet of Things;
The sensor is essentially a detection device that is used to collect various types of information and convert it into a specific signal. It can collect information such as identity, pressure, temperature, humidity, light, sound, smell and so on. Commonly used sensors can be divided into three categories: physical sensors, chemical sensors, and biosensors. The sensor industry is currently dominated by several leading companies in the United States, Japan, and Germany, and representative companies in China's sensor market include Hanwei Electronics, Goer shares, Gaode Infrared, Naiwei Technology, Huagong Technology, and Yuanwang Valley. Wait.
(3) Wireless module manufacturers: the key to achieve networking and positioning
The wireless module can be divided into two major categories: communication module and positioning module. Common LAN technologies include WiFi, Bluetooth, ZigBee, etc. Common WAN technologies mainly include 2/3/4G, NB-IOT and unlicensed bands of LoRa, SigFox, and other technologies working in licensed bands. Different communications correspond to different technologies. Communication module. At present, foreign companies still dominate the wireless module, including Telit, SierraWireless and so on. Domestic manufacturers are also relatively mature, able to provide complete products and solutions, including Huawei, ZTE, Huanxu Electronics, Mobile Communications, Corecom, and China Mobile Internet of Things.
(4) Network operators: the channels that control the Internet of Things;
Network operators are the most mature link in the IoT industry chain. The Internet of Things network refers to a converged network formed by various communication networks and the Internet, including cellular networks, local self-organizing networks, private networks, etc., and thus relates to communication devices, communication networks, SIM manufacturing, and the like. The Internet of Things can largely reuse existing telecom carrier networks, such as cable broadband networks and 2/3/4G mobile networks. It is an important promoter of the development of the domestic Internet of Things. Therefore, this session will focus on the three major telecom operators and closely related SIM card manufacturers, such as Eastcom Peace, Hengbao, Tianyu Information.
(5) Platform service providers: improve the effective management of the Internet of Things;
As an important part of equipment aggregation, application service and data analysis, the Internet of Things platform not only implements the “management, control, and battalion†of the terminal, but also provides PaaS services for application development, service and system integration. According to different platform functions, it can be divided into three types: device management platform, connection management platform and application development platform. Foreign platform vendors include Jasper and Wylessy. There are mainly three types of manufacturers in the domestic IoT platform enterprises. One is the three major telecom operators, which mainly starts with building a connection platform. The other is Internet vendors such as BAT and JD. They use their traditional advantages to build equipment management. And application development platform; third, platform vendors in their respective segments, such as Yitong Century, Hetai, Shanghai Qingke.
(6) System and software developers: to create the arteries of the Internet of Things;
The Internet of Things system and software generally include operating systems, application software, etc., which can make IoT devices operate effectively. Among them, the operating system (OS) is a program that manages and controls IoT hardware and software resources, and is the most basic system software. Other applications are supported by the operating system. At present, the main issues of the IoT operating system are some IT vendors, such as Google, Microsoft, Apple, Huawei, and Ali. Application software development mainly focuses on areas with strong versatility such as car networking, smart home, and terminal security, such as Shenglu Communication, Haier, and Venus.
(7) Intelligent hardware manufacturers: providing terminal bearers of the Internet of Things;
Smart hardware is a device that integrates sensor components and communication functions to access the Internet of Things and implement specific functions or services. According to the customer-oriented purchase, it can be divided into 2B and 2C categories. Class 2B includes metering, such as smart water meters, smart gas meters, smart meters, industrial monitoring instruments, etc., vehicle front loading, industrial equipment and public service monitoring equipment; 2C mainly refers to consumer electronics, such as wearable devices, Smart home, etc. The 2B manufacturers with relatively concentrated terminal production enterprises include Sanchuan Wisdom, Xintian Technology, and Hanwei Electronics.
(8) System integration and application service providers: implementers of IoT applications;
System integration is the process of identifying and integrating multiple products and technologies into a complete solution based on the requirements of a complex information system or subsystem. At present, mainstream system integration practices include device system integration and application system integration. Facing the complex application environment of the Internet of Things and equipment in many different fields, system integrators can help customers solve various types of equipment, subsystem interfaces, protocols, system platforms, application software, etc. with subsystems, building environment, construction coordination, Organization management and staffing related issues ensure that customers receive the most appropriate solution. At present, relevant domestic system integration and application service providers include Huawei, ZTE, Yuanwang Valley, and Hanwei Electronics.

Internet (English: internet), also known as the Internet, or the Internet, the Internet, the Internet began in 1969 in the United States. It is a huge network that is connected in series between the network and the network. These networks are connected by a common set of protocols to form a logical single large international network. Usually the Internet refers to the Internet, while the Internet refers to the Internet. This method of interconnecting computer networks can be called "network interconnection". On this basis, a global Internet that covers the whole world is called the Internet, that is, a network structure that is connected to each other. The Internet is not the same as the World Wide Web. The World Wide Web is just a global system based on hyperlinks and is one of the services that the Internet can provide.
The difference between the Internet of Things and the InternetInternet: People want to know something about the Internet. Someone needs to collect this information and upload it to the Internet for people to browse. People need to do a lot of work in it, and it is difficult to dynamically understand the changes.
Internet of Things: The Internet of Things is an extension of the Internet. Through various sensing devices, such as radio frequency identification, sensors, infrared, etc., information is transmitted to the receiver, and then transmitted through the Internet. Information processing is performed through high-level applications to achieve remote monitoring and automatic Alarm, control, diagnosis and maintenance to achieve the integration of “management, control and operationâ€.
In fact, the application of the Internet of Things has been extensive, covering public security, traffic management, military defense, environmental protection, energy and power, industrial monitoring, logistics management, medical health, smart home and other fields.
One of the differences between the Internet and the Internet of Things: the ecosystem path and structure are completely different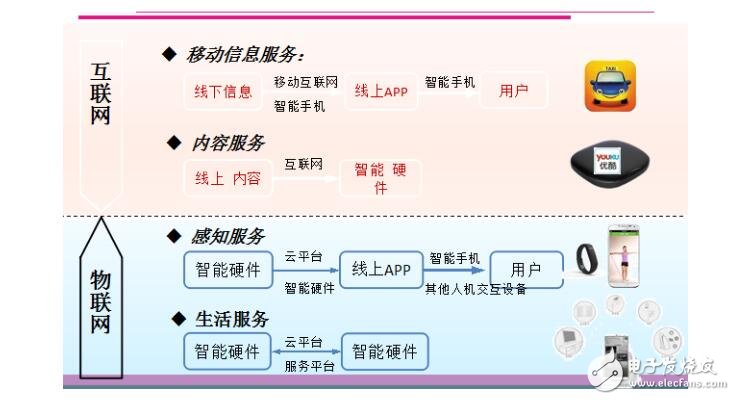

Embed Scan Module,Embedded 2D Barcode Scanner,Wide Range Bar Code Reader,Barcode Scanner 360
Guangzhou Winson Information Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.barcodescanner-2d.com