Determination of heavy metals in soil by ICP-2060T
ICP-2060T
Determination of heavy metals in soil
Abstract: The sample is digested by heating acid to
ICP-2060TDetermination of copper, zinc, nickel, lead, cadmium, chromium. The method is applied to the determination of copper, zinc, nickel, lead, cadmium, chromium and arsenic in soil samples, and the pretreatment process is simple, the equipment is simple, and the cost is low. The experimental results show that when the method is applied to the determination of heavy metals in soil, the determination results are accurate and reliable, and the repeatability is good.
1Foreword
As the main carrier of agricultural production and an important part of the ecological environment, soil quality is closely related to people's life. With the development of the economy, a large amount of untreated waste containing heavy metals is discharged into the environment, making The farmland soil environment and crops have been polluted and destroyed to varying degrees, which in turn endangers human health and even life through the food chain. Therefore, the problem of heavy metal pollution in soil has become an increasingly serious ecological problem. Analytical determination of heavy metals in soil, before sample
Processing is the key. In this paper, the hot plate heating method is used for pretreatment of soil samples.
ICP-AES
The content of copper, zinc, nickel, lead, cadmium and chromium is determined, the method is simple, safe, low cost, and the test result has high accuracy and precision.
Experimental part
2.1Main instruments and reagents
2.1.1instrument
ICP-2060TInductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometer, Jiangsu Tianrui Instrument Co., Ltd.;
BS224SElectronic balance, Sartorius Scientific Instruments (Beijing) Co., Ltd.;
EPED-40TLaboratory-grade ultra-pure water machine, Nanjing Yipu Yida Technology Development Co., Ltd.;
EG35AType electronic temperature control heating plate, Beijing Laibo Tyco Instrument Co., Ltd.; pipetting gun (
10-100uL,
100-1000uL) Two, Prand, Germany.
The polytetrafluoroethylene beaker and the plastic volumetric flask used are all made of nitric acid (
1+1Soak overnight, rinse directly with ultrapure water before use, and dry naturally before use.
2.1.2Reagent
The experimental water is ultrapure water; the experimental acid is excellent grade pure acid: hydrochloric acid, nitric acid, hydrofluoric acid, perchloric acid
Soil standards are provided by the State Environmental Protection Administration Standards Institute
Standard material: standard solution of copper, zinc, nickel, lead, cadmium, chromium (
1000mg/L) provided by the National Nonferrous Metals Analysis and Testing Center.
2.2experimental method
2.2.1Preparation of sample test solution
Accurate weighing
0.2-
0.3g(accurate to
0.0001gSample
50mLIn a Teflon beaker, wet with water and then add
10mLHydrochloric acid, heated at a low temperature on a hot plate in a fume hood, causing the sample to be initially decomposed and to be evaporated to about
3 mLWhen you take it, take a little cold and then join
5 mLNitric acid,
5 mLHydrofluoric acid,
3 mLPerchloric acid, after heating, heating on a hot plate at medium temperature
1After about an hour, then open the lid and continue to heat the silicon. In order to achieve a good flying silicon effect, the beaker should be shaken frequently. When heated to a thick white smoke of perchloric acid, it is capped to decompose the black organic carbide. After the black organic matter on the inner wall of the beaker disappears, the lid is opened, the white smoke is driven away, and the contents are viscous, and the content can be supplemented depending on the digestion.
3 mLNitric acid,
3 mLHydrofluoric acid,
1 mLPerchloric acid, repeat the above digestion process. When the white smoke is exhausted again and the contents are viscous, remove the cooling, rinse the inner wall and lid with water, and add
1 mL(
1+1The nitric acid solution warms the residue. Then transfer the whole amount to
50 mLIn the volumetric flask, after cooling, make up to the line and shake it for testing. At least one parallel sample is guaranteed for each sample, and a blank solution is prepared by using water as a sample, and at least one sample is prepared in each batch.
2More than one blank solution.
2.2.2Calibration curve
Accurate preparation
0,
0.2,
0.5,
1.0,
2.0,
3.0mg/LStandard solution of copper, zinc, nickel, lead, cadmium, chromium, stable in the instrument
30minThe standard solution is measured and the calibration curve is drawn.
2.2.3Sample determination
According to the table
1Set instrument parameters:
table1 ICP-AES working conditions
use
ICP-2060T The emission intensity of the element in the sample is measured, and the element concentration is calculated by a calibration curve.
Results and discussion
3.1Sample weight affects test results
Figure
1For the same soil sample, the relationship between different weighing weight and test results, as can be seen from the figure, when the sample weight is greater than
0.2gWhen the test results are stable. In order to reduce the influence of the matrix effect while ensuring the accuracy and precision of the method, the weighing weight of the method sample is
0.25gabout.
Figure 1 Total sample and test results 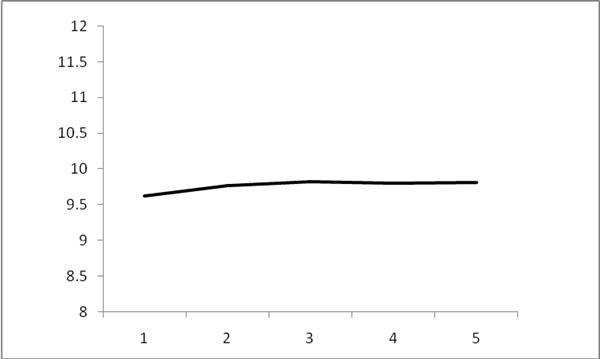
3.2
Method detection limit and linear range
The linear range, method sensitivity, instrument detection limit and method detection limit of each heavy metal element working curve were determined through several experiments.
By table
2It can be seen that the fitting coefficients of the working curves of the heavy metal elements are higher than
0.999, indicating that the linear relationship is good in the linear range of the working curve. Since the operating parameters of the instrument are optimized, see table
1To maximize the sensitivity of element excitation. The detection limit of the instrument and the detection limit of the method are all low, further indicating that the experimental conditions of the method are reliable (Table
2).
table2
ICP-2060T
Determination of linearity, sensitivity, and detection limit of heavy metals in soilPrecision and accuracy of the method
Parallel treatment of soil reference materials
6Parts, determine the content of heavy metals, and calculate the relative standard deviation of the results (
RSD%) to evaluate the precision of the method.
table
3ICP-2060T
Determination of the results of the determination of the standard by the heavy metal method of soil (
n=6)
By table
3It can be seen that the method is used to determine soil samples.
6The recovery rate of heavy metals is in the range of
94.1-
106.9Relative standard deviation
RSD%) are smaller than
5% It shows that the precision of the method is high, the measurement result is stable, and the experimental conditions in the analysis process are easily controlled.
in conclusion
The experimental results show that the method can be used in soil samples when the composition of the soil sample matrix is ​​complex.
6The heavy metal elements are simultaneously digested, and the effect is ideal.
Optimized by the ideal pre-processing method and instrument state
ICP-AESWhen measuring the content of copper, zinc, nickel, lead, cadmium and chromium in soil samples, it has high sensitivity, precision and accuracy. The determination results are accurate and reliable. The experimental conditions in the analysis process are easy to control and can meet the soil analysis. Claim.
Conecting Terminals Without Screws
Conecting Terminals Without Screws,Cold Pressing Terminals,Low Pressure Cold Shrinkage Terminal,Cold Shrinkage Cable Terminals
Taixing Longyi Terminals Co.,Ltd. , https://www.longyiterminals.com