What, why, how... six FAQs for low noise instrumentation amplifiers
A low-noise instrumentation amplifier is a very sensitive device that measures very weak signals in noisy environments or with high voltages of no interest. The amplifier measures the signal by suppressing the common-mode voltage at the two inputs and amplifying the difference between the input signals.
The low noise instrumentation amplifier has very low broadband noise and low 1/f noise corner frequency, so it can meet the needs of most precision applications. So, before you're ready to design a high-performance system with a low-noise instrumentation amplifier, you may need to know ahead of these issues—
Which system requires a low noise instrumentation amplifier?
Typically, low noise instrumentation amplifiers are used in systems that require precision amplification and require sensor signal conditioning. The signals generated by such systems are too weak to be used directly by the data converter. The narrowband signals generated by some sensors may be very weak, while others may produce time-varying signals of various frequencies over a wide bandwidth. In both cases, these signals need to be amplified above the noise floor of the system. . At high common-mode voltages (usually AC line frequency), the system must maintain its proper performance in noisy environments.
What application needs to use this amplifier?
Low noise instrumentation amplifiers address some of today's toughest challenges. These challenges require precision amplification of signal monitoring, data analysis, and physical measurement tools. Their applications are as follows:
Data logging system for mining and energy mining
Surgical instruments required for cardiac catheter ablation for arrhythmia
Modal vibration analysis tool for improving the safety of machinery and vehicles
Other applications include mic preamps, sonic transducers, piezoelectric sensor conditioning, blood pressure monitors, brain tumor diagnostics (EEG), cardiac monitors (ECG), magnetic sensor conditioning, and power monitors.
How do I determine the noise specification of an instrumentation amplifier?
Like an op amp, an instrumentation amplifier specifies noise to be converted to input noise (RTI). That is to say, all appear at the input of the amplifier. But unlike op amps, instrumentation amplifiers also have output stage noise (eno) that must be divided by the gain to obtain the RTI value. The noise (RTO) that is converted to the output of the amplifier is equal to the product of the RTI noise and the gain of the amplifier.
How to calculate the total noise density?
A simple noise model for an instrumentation amplifier is shown in Figure 1. To get the total noise, you must consider the source resistance at the input of the amplifier. Any sensor connected to the instrumentation amplifier has an output resistor, and the resistance value may vary greatly depending on the type of sensor. Series resistors are used to protect the instrumentation amplifier. The sum of these resistors forms the total source resistance (expressed in RS), see Figure 1.
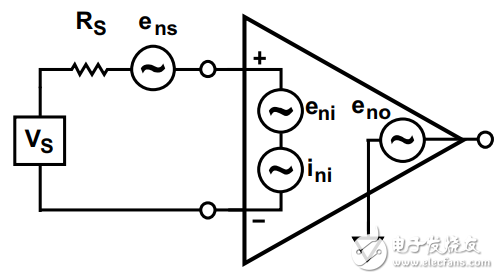
Figure 1. Simple instrumentation amplifier noise model
The effect of this resistance on noise has two aspects. No matter how well-made resistors are produced, they produce very low thermal noise, which is proportional to the square root of the resistance. In addition, current noise (ini) can be converted to voltage noise by RS.
Therefore, the three main sources of noise are:
Voltage noise unrelated to RS (eni and eno)
Source resistance thermal noise (ens)
Current noise (ini)
Combine these noises to get the total noise density, which is calculated as follows:
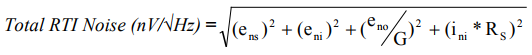
How to choose the low noise instrumentation amplifier that best meets the needs of the application?
The instrumentation amplifier with the lowest input voltage noise value (nV/√Hz) is not necessarily the best low noise instrumentation amplifier. In noise sensitive applications, the gain, source resistance, and frequency range must be considered in order to find the best amplifier.
Figure 2 shows the total noise of the three ADI instrumentation amplifiers to provide optimum noise performance with almost all source resistance.
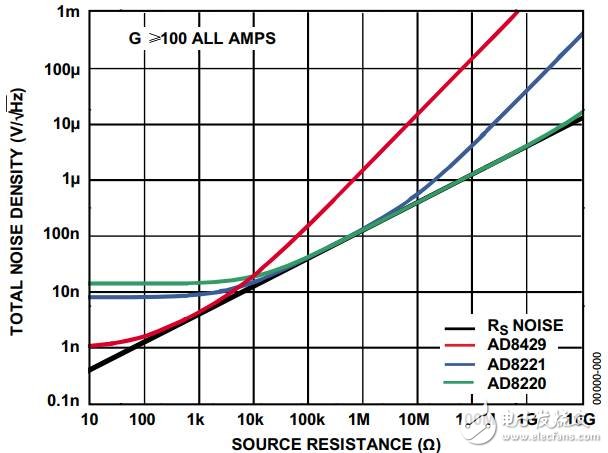
Figure 2. Relationship between total noise and source impedance
Note that no matter which amplifier is selected, when the RS value is low, the voltage noise is the main noise, and when the RS value is high, the current noise is the main noise. Given the source resistance value, the following equation can be used to determine which noise is the dominant noise.
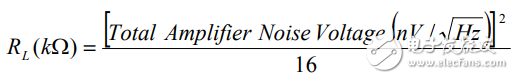
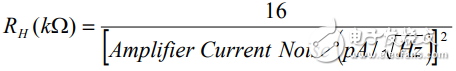
If the source resistance is lower than RL, the voltage noise is the dominant noise. In this case, an amplifier with a lower voltage noise should be selected. If the source resistance is higher than RH, the current noise is the main noise. In this case, the amplifier with lower current noise should be selected.
In the above example, when the RS value is between 5 kΩ and 10 kΩ, the noise performance of these amplifiers will be very close, or even the same. At this time, you need to consider other parameters of the optimization system (such as: bandwidth, power, distortion, cost).
Can I build a low noise instrumentation amplifier myself?
You can build your own discrete low noise instrumentation amplifiers, but you must overcome some of the difficulties. For example: high common mode rejection, low drift, high bandwidth, and low distortion must be guaranteed. It is quite difficult to implement these parameters in a discrete design. A variety of devices must be used. The cost of adjustment is very high, the power consumption is high, and the area occupied by the board is relatively large. The low noise instrumentation amplifiers offered by ADI provide a better solution for a variety of applications.
Genki Ippai 1.0 uses high-tech temperature control, food grade pod and high-quality material device. We also upgrade to type-C interface for charging faster. We have developed various flavors for Genki Ippai Pod Systems. Up to 11 flavors provide consumers with more choices. What's more, you can use other brand`s vape pen with our vape pod.
We offer low price, high quality Disposable E-Cigarette Vape Pen,Electronic Cigarettes Empty Vape Pen, E-cigarette Cartridge,Disposable Vape,E-cigarette Accessories,Disposable Vape Pen,Disposable Pod device,Vape Pods to all over the world.
GenkiIppai Pods 1.0,Pod Systems Vape And Smoke,Vape Pod System Device,Pod System Vape Kit,Pod System Mini Vape Pod
ZGAR INTERNATIONAL(HK)CO., LIMITED , https://www.zgarpods.com