Those things about mobile phones and the Internet
We are more and more inseparable from smartphones, watching mobile phones while waiting for a car, watching mobile phones while eating, watching mobile phones while dating, watching mobile phones before going to sleep... You may not know about some things about mobile phones and the Internet. As a communications engineer, we always wanted to do a science project, and hope that the following content will let you know more about your smartphone. . .

1
Those logos on the phone
Turn on the phone, usually we will see some of the following logos. . .
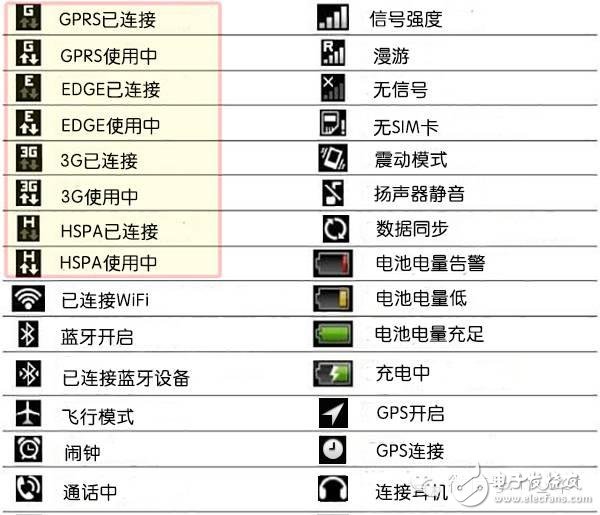
What do the letters G, E, 2G, 3G, H, 4G and so on next to the signal strength indicator mean?
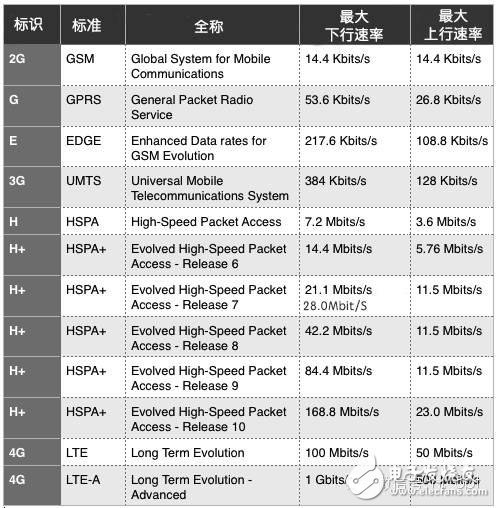
2G, G, and â€E belong to the second generation mobile communication technology. The 2G technology standard is basically divided into two types: GSM and CDMA. Among them, EDGE (E) and GPRS (G) are upgraded versions of GSM.
2G, on behalf of GSM, the maximum uplink and downlink speed is only 14.4Kbps.
G, on behalf of GPRS, refers to the 2.5G network. At this time, the network speed is slow, and the maximum downlink speed is only 53.6Kbps.
â€E, which stands for EDGE network, is a 2.75G network. The network speed is faster than GPRS, and the maximum downlink speed is 217.6Kbps.
3G, H, H+, refers to the enhanced version of 3G network and 3G network, belonging to the third generation mobile communication technology.
According to the communication standard, H+ can reach the highest downlink rate of 168.8 Mbps. However, due to the evolution of LTE technology, most 3G networks have not completed subsequent upgrades, and the highest downlink rate of H+ is usually 42.2 Mbps.
In addition, T stands for TD-SCDMA and also refers to 3G network, which is called TIme Division-Synchronous Code Division MulTIple Access. It is the third generation mobile communication standard (referred to as 3G) proposed by China and is also approved by ITU. One of the three 3G standards.
3G has three standards: CDMA2000, WCDMA, and TD-SCDMA. The UMTS (Universal Mobile TelecommunicaTIons System) mentioned in the above table refers to the technical specifications and protocols of the entire 3G mobile communication network, including the core network and the wireless network, and WCDMA is the air interface technology of the wireless network. Refers to the technology used by base stations and mobile terminals, belonging to the wireless network, and TD-SCDMA is also the air interface technology.
Next, we will introduce the 4G that everyone is using. .
2
3.9G —†4G —†4.5G
LTE does not represent 4G.
What is LTE?
LTE (Long Term EvoluTIon) is a long-term evolution plan of the UMTS (Universal Mobile Telecommunications System) technical standard developed by the 3GPP (The 3rd Generation Partnership Project).
For LTE, 3GPP currently has a standard of five versions from Release-8/9/10/11/12, and will be upgraded to Release-13/14/15/16.
The 3GPP Release-8/9 version is not 4G. It usually refers to 3.9G. The 3GPP officially calls it LTE. Its logo is like this:

The 3GPP Release-10/11/12 version is officially known as LTE-Advanced. This is what we usually call 4G. Its logo is like this:

The 3GPP Release-13 version has basically completed the standardization work. Its official name is LTE-Advanced pro. This is what we usually call 4.5G (or 4G+). Its logo is like this:

We have now entered the 4G+ era, marking the mobile Internet speed is moving towards 1Gbps.
As for the later Release-15/16, it is expected that 5G technology will be introduced.
3
Don't be fooled by your cell phone signal
Media Converter And Optical Fiber Switch
Media Converter Optical Fiber Switch fiber optic switcher
Media Converter,Optical Fiber Switch,Fiber Optic Switcher
Chinasky Electronics Co., Ltd. , https://www.chinacctvproducts.com